Are you a person who is planning to switch into the field of Analytics but confused about what roles you wanted to pursue your career in? Well, you are at the right place. This article is targeted at a newbie audience who are planning to make a move into this field. We have collated the different roles in Data science and analytics, the skill sets required for the role, and the nature of the work the respective role does. In the earlier article, we have explained the life cycle of data science and we recommend reading it as well.
Before attempting some hard-and-fast role definitions of these data science careers, then, let us start by sketching out the different task sets you would typically find on a data science team. The idea here is to scope the high-level competence areas that need to be covered on a data science team, regardless of who carries out which task.
The three main data science careers are:
- Mathematics/Statistics
- Computer Science
- Business domain knowledge.
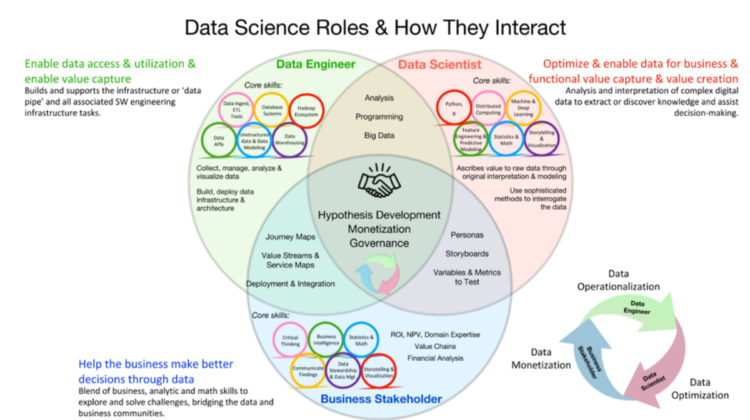
Competence areas needed on a data science team.
The image above shows the easy part because there’s general agreement on which competencies are required for a successful and efficient data science career though you still need to define the roles and areas of responsibility for each team member. The definitions of data science career that you find here aim to give you a general understanding of the most important roles you will need on your data science team. Just remember that variants may apply, depending on your own specific setup and strategic focus.
Some companies require you to know all the skills of all these positions, but as your team grows at your company, you may find that certain people will focus on their strengths to ultimately solve the most problems with Data Science and therefore become specialized in one of the roles below.
- Business Analyst
- Database Administrator
- Big Data Engineer/Data Architect
- Data Analyst
- ML Engineer
- Business Intelligence (BI) Developer
- Business Intelligence Analyst
- Statistician
- Data Scientist
- Computer Vision(CV) Engineer
- Natural Langauge Processing(NLP) Engineer
- MLOps Engineer
The role of business analysts is slightly different from other data science jobs. While they do have a good understanding of how data-oriented technologies work and how to handle large volumes of data, they also separate the high-value data from the low-value data. In other words, they identify how Big Data can be linked to actionable business insights for business growth.
Although many of their job tasks are similar to that of data analysts, business analysts are experts in the domain they work in. They try to narrow the gap between business and IT. Business analysts provide solutions that are often technology-based to enhance business processes, such as distribution or productivity.
Organizations need these “information conduits” for a plethora of things such as gap analysis, requirements gathering, knowledge transfer to developers, defining scope using optimal solutions, test preparation, and software documentation.
Roles & Responsibilities:
- Business analysts identify business needs, crystallizing the data for easy understanding, manipulation, and analysis via clear and precise requirements documentation, process models, and wireframes. They identify key gaps, challenges, and potential impacts of a solution or strategy.
- In a day, a business analyst could be doing anything from defining a business case or eliciting information from top management to validating solutions or conducting quality testing. Business analysts need to be effective communicators and active listeners, resilient and incisive, to translate tech-speak or statistical analysis into business intelligence.
- They use predictive, prescriptive, and descriptive analyses to transform complex data into easily understood actionable insights for the users. A change manager, a process analyst, and a data analyst could well be doing business analysis tasks in their everyday work.
Skills Required:
- Apart from a degree in business administration in the field of your choice, say, healthcare or finance, aspiring business analysts need to have knowledge of data visualization tools such as Tableau and requisite IT know-how, including database management and programming.
- You could also major in computer science with additional courses that include statistics, organizational behavior, and quality management. Or you could get professional certifications such as the Certified Business Analysis Professional (CBAP®) or PMI Professional in Business Analysis (PBA). Many universities offer degrees in business intelligence, business analytics, and analytics. Check out the courses in the U.S/India
How to Become a Business Analyst?
Business analysts act as a link between the data engineers and the management executives. So, they should understand business finances and business intelligence, and also the IT technologies like data modeling, data visualization tools, etc
